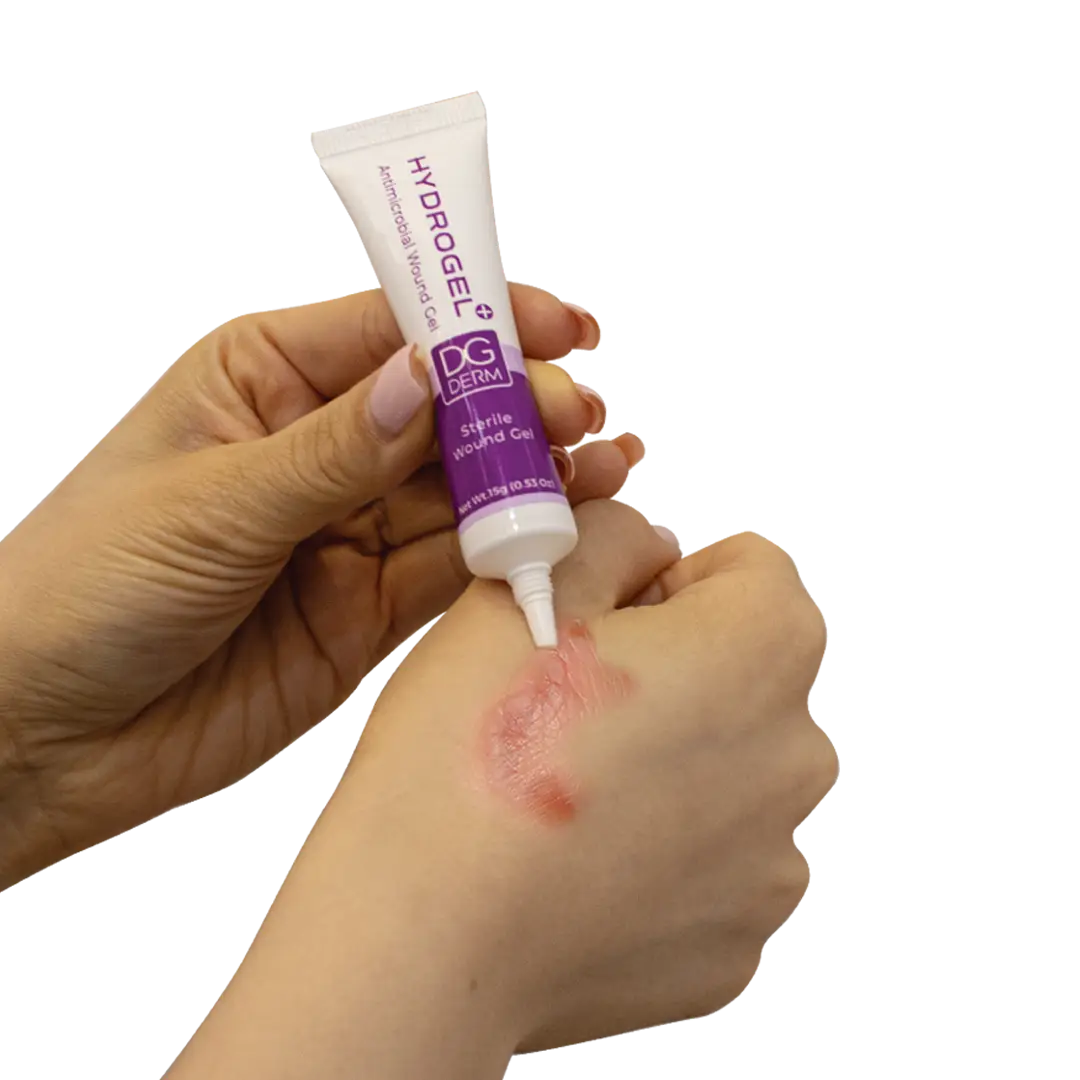
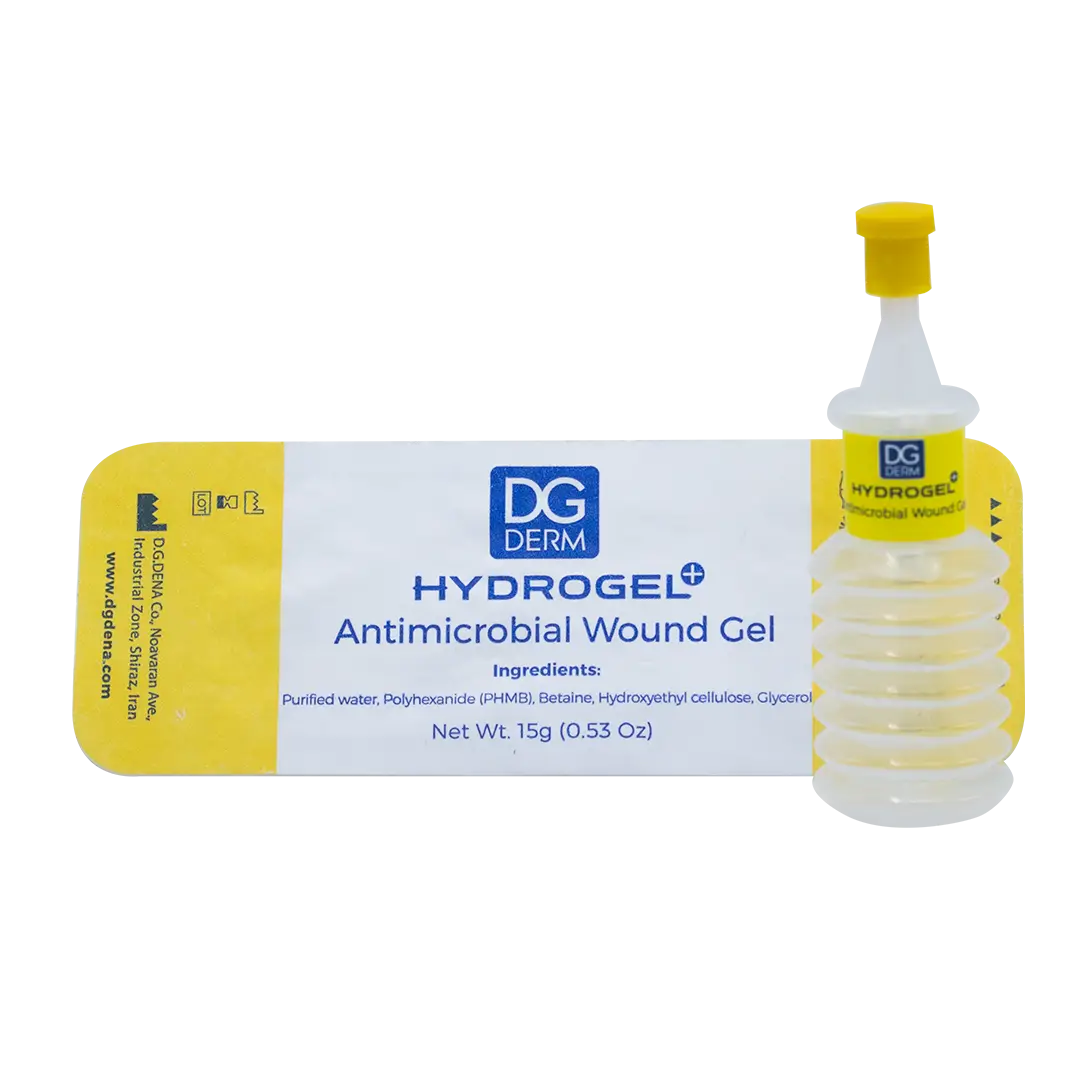
DG Derm antimicrobial wound hydrogel
DG Derm antimicrobial wound hydrogel is capable of destroying various microorganisms, including gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, even its treatment-resistant type such as MRSA, VRE, fungi, and viruses, in a short time with effective ingredients such as PHMB and betaine in its formulation. On the other hand, it is capable of trapping water, providing moisture to the slough and necrotic tissues, while reducing the wound site temperature, loosening and separating these tissues with its special structure via a stable three-dimensional polymer network, it also helps reduce unpleasant wound odor by absorbing secretions, providing greater comfort for the patient.
DG Derm Antimicrobial Hydrogel Usage
- Traumatic wounds
- Diabetic foot ulcers
- Venous ulcers
- Types of burns
- Abrasions and cuts
- Post-surgical wounds
- Radiation wounds
- Bedsores
- Wounds caused by contact with chemicals such as acids and bases
Ingredients
Purified water, hydroxyethyl cellulose, glycerol, polyhexanide, betaine
Polyhexanide (PHMB)
Among the various raw materials with antimicrobial properties, polyhexanides, which are present in the DG Derm antimicrobial hydrogel product, have been introduced as the most effective and fastest-acting compounds for combating various microorganisms.
These compounds are linear polymers composed of cationic biguanide groups linked to hexamethylene chains. Their structure closely mimics the structure of antimicrobial peptides, making them highly effective against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, antibiotic-resistant strains, viruses, fungi, and yeasts. Due to their versatile antimicrobial properties, they have extensive applications in managing both acute and chronic wounds with low to moderate exudate levels.
Polyhexanide is fully biocompatible and does not cause cellular damage. Its unique chemical and electrostatic properties make it an ideal compound for wound care. It effectively prepares the wound site and plays a crucial role in the treatment and prevention of wound infections. The mechanism of action involves polyhexanide binding to the microbial cell membrane, disrupting its functional metabolism. This interaction leads to structural changes and ultimately results in the microbial cell destruction.
Overall, polyhexanide stands out as a highly effective and safe option without causing allergies, edema or anaphylaxis for wound management, offering both therapeutic and prophylactic benefits.
Betaine
Another key component in DG Derm antimicrobial hydrogel is betaine, an amphoteric surfactant. Betaine binds to microbial and biofilm membranes via its hydrophobic tail, disrupting cells by reducing surface tension, while its hydrophilic head suspends and removes contaminants. This prevents re-contamination and infection. Betaine also maintains optimal hydration, creating a moist healing environment, and minimizes irritation due to its low cytotoxicity. These properties make it ideal for chronic wounds and sensitive skin, enhancing the hydrogel’s cleansing, protective, and healing capabilities.
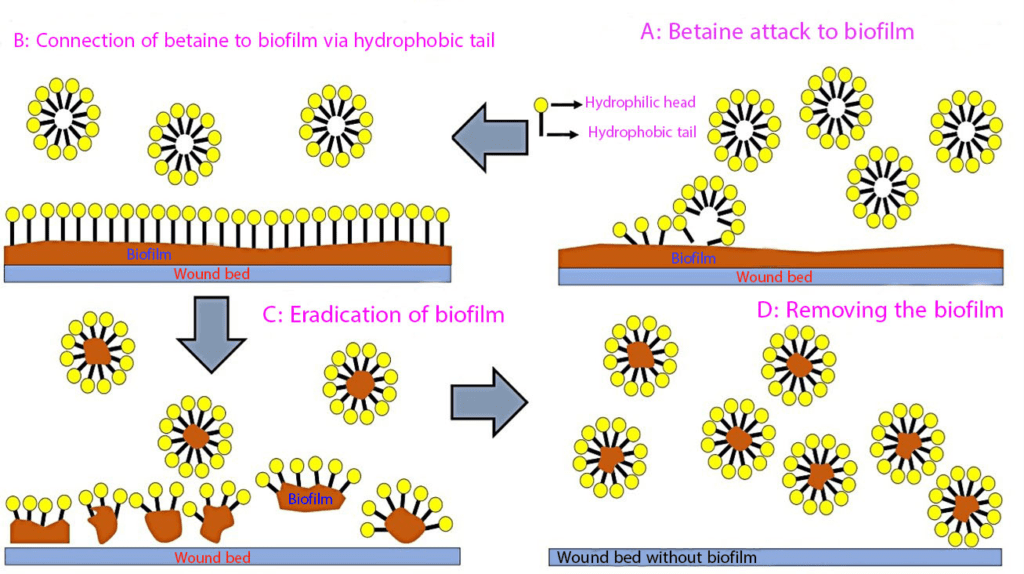
Betaine and polyhexanide synergic effect
Studies show that betaine and polyhexanide work synergistically to enhance antimicrobial efficacy, delivering improved, faster, and longer-lasting effects. Betaine creates an optimal platform for polyhexanide by reducing surface tension and disrupting microbial cell walls, enabling deeper penetration into biofilms. This synergy boosts the product’s ability to decontaminate wound sites effectively. Betaine’s amphoteric nature also ensures compatibility with polyhexanide, forming a powerful antimicrobial duo that significantly enhances the product’s infection-fighting capabilities.
Hydroxyethyl cellulose
In addition to polyhexanide and betaine, DG Derm Antimicrobial Hydrogel is also composed of a cellulose-derived polymer called hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC), which provides the appropriate viscosity for application on wounds as a primary dressing by modifying the rheology of the product.
In addition, hydroxyethyl cellulose provides product stability and allows the hydrogel dressing to be maintained at the wound site for several days without disintegration.
Also, it enhances the moisturizing and absorption the wound properties, promoting better debridement, effective cell migration, and tissue epithelialization due to its exceptional moisture retention properties.
DG Derm Antimicrobial Hydrogel Evaluation for Biofilm Inhibition and Eradication
DG Derm hydrogel biofilm inhibition property was conducted based on the national standard 16684 in order to investigate the product effectiveness in preventing the microbial biofilm formation on the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and showed that the product is able to inhibit the biofilm formation by the two bacteria with high efficiency.
The biofilm eradication capability was conducted based on the ASTM standard E2799-17 in order to investigate the product effectiveness in eliminating microbial biofilm on the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and showed that the product is able to destroy biofilm on both bacteria with high efficiency and very good performance even at medium dilutions. The results can be seen in the graphs below.
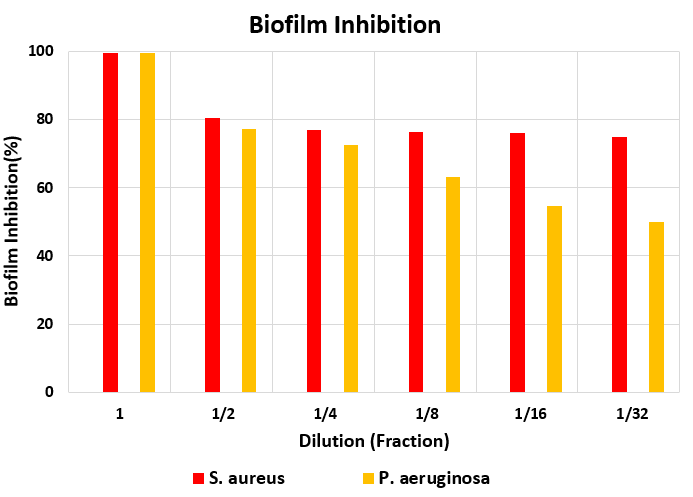
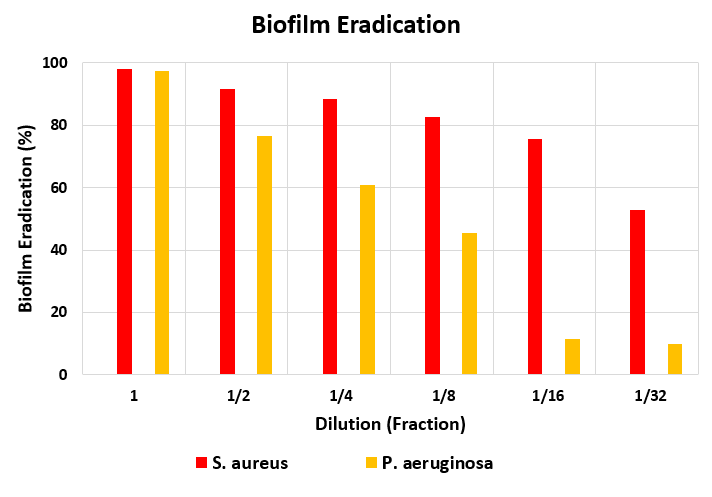
Investigating Biofilm Inhibition and Eradication by DG Derm Antimicrobial Hydrogel
Studying Resistant MRSA and VRE Microbial Count Reduction and Effectiveness Speed
This test was conducted based on USP 51 standard to investigate the microorganism’s reduction using the CFU count method on two resistant bacteria, and the results showed that the product succeeded in eliminating both types of bacteria in a short period (about an hour). Therefore, based on this test, as soon as the product is used, its antimicrobial effects begin quickly, and it is able to reduce the microbial count to zero in a short time. In this regard, it can be considered a fast-acting product even against resistant microorganisms. The results of these tests are shown in the graphs below.
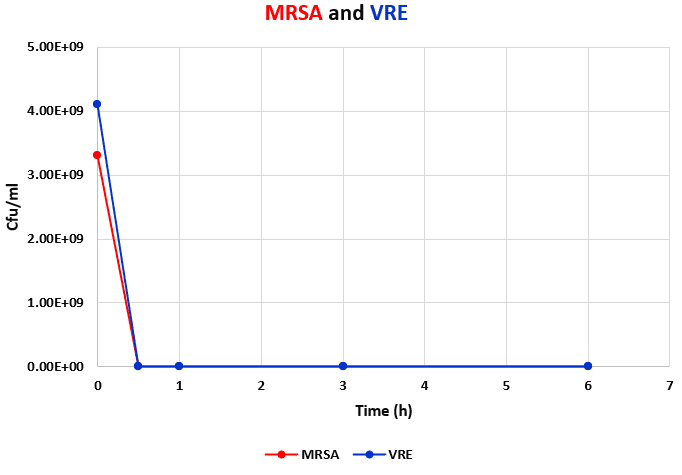
Investigating MRSA and VRE Eradication Properties
How to use DG Derm Antimicrobial Hydrogel
DG Derm Antimicrobial Hydrogel can be applied directly to the wound site or by soaking it in a secondary dressing. If necessary, the product can be gently spread with a suitable sterile applicator. For cavity wounds, fill the wound with the dressing and then use the secondary dressing. Make sure to close the product cap immediately after use. Avoid contact between the tube tip and the wound, body parts, or contaminated surfaces. Do not use this product continuously for more than 30 days. If no improvement occurs, consult a specialist.