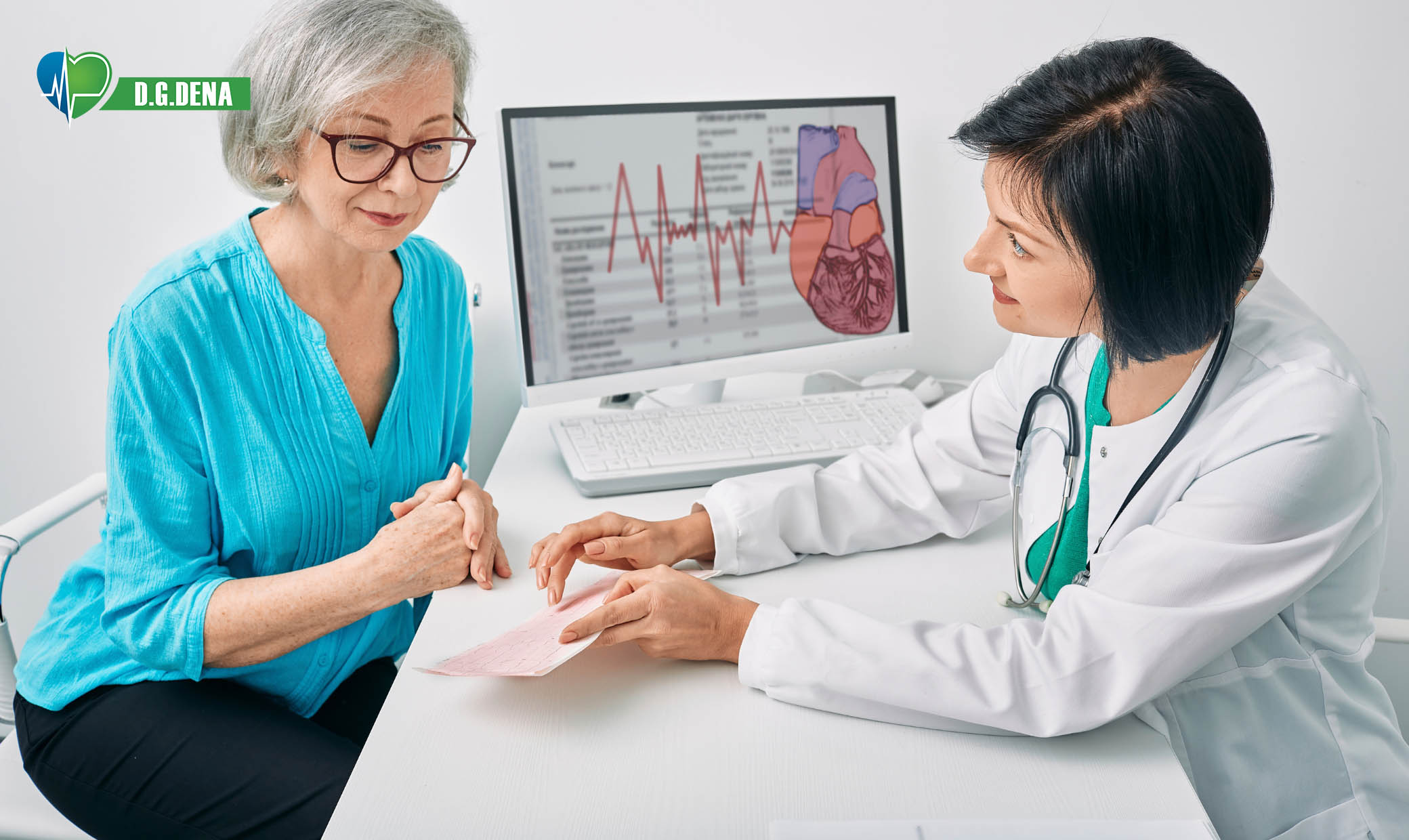
What is an Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)?
An electrocardiogram, commonly abbreviated as ECG or EKG, is a harmless, painless test that plots the electrical currents of your heart. It is the most common diagnostic test in cardiology, and it helps doctors diagnose heart rhythm disorders, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular diseases. As a patient scheduled for an ECG, a medical student, or one who just wants to learn about heart health, this manual provides everything you would like to learn.
How Does an Electrocardiogram (ECG) Work?
Your heart is pumping because of electrical impulses that lead to contractions of muscles. The ECG machine measures the impulses using electrodes on your arms, legs, and chest. The test records the signals as waveforms, which are read by doctors to assess the performance of your heart.
Important ECG Wave Components:
- P Wave: Indicates atrial depolarization (upper chambers contracting).
- QRS Complex: Indicates ventricular depolarization (lower chambers contracting).
- T Wave: Represents ventricular repolarization (the heart unwinding itself in preparation for the next beat).
- U Wave (if present): May suggest electrolyte imbalance or cardiac disease.
Why is an ECG Test Important?
An electrocardiogram is an essential diagnostic tool for the prevention and detection of life-threatening heart abnormalities, including:
- Arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythm) determine atrial fibrillation (AFib), bradycardia (slow heart rate), or tachycardia (fast heart rate).
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction) uncovers obstructed arteries or previous heart injury.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) restricts blood flow to the heart.
- Heart Failure, uncover enlarged or damaged heart muscles.
- Structural abnormalities detect thickened heart walls or birth abnormalities.
Types of Electrocardiogram
- Resting ECG: Taken while in a reclined position; assesses normal cardiac function.
- Stress Test (Exercise ECG): Tests heart during exertion (treadmill/cycle).
- Holter Monitor: 24-48 hour ambulatory ECG worn to monitor occasional symptoms.
- Event Monitor: Records heart activity for weeks, turned on only during symptoms.
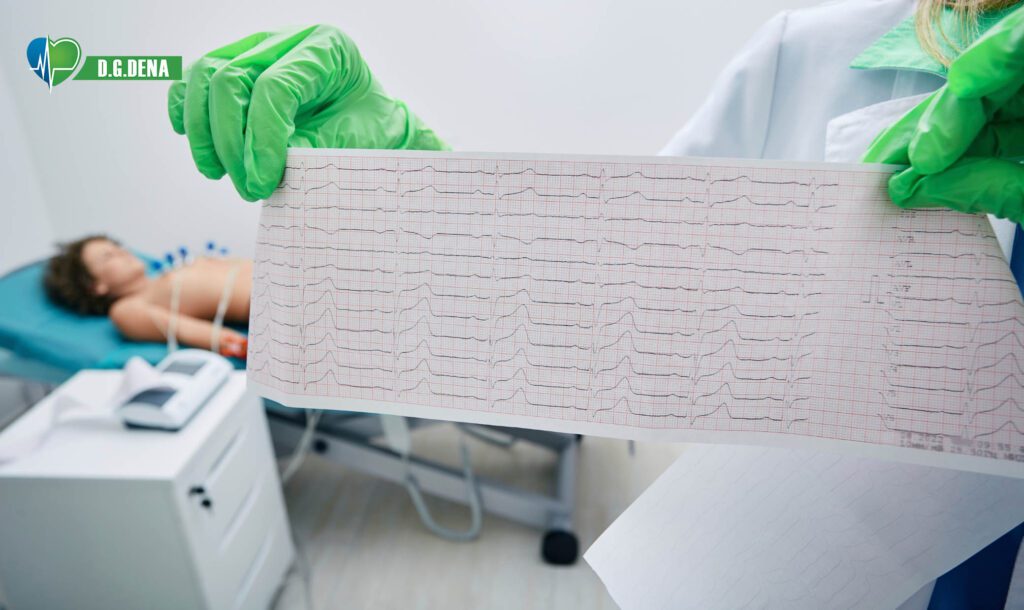
What to Do Before and During an Electrocardiogram ?
Before the Test:
- Avoid oily skin creams (can interfere with electrode contact).
- Wear loose clothing to allow easy placement of electrodes.
- Take off metal objects (jewelry, watches) to avoid interference with signals.
During the Test:
- A technician attaches 10-12 sticky electrodes to your chest, arms, and legs.
- The ECG machine records heart signals for 5-10 minutes (painless and quick).
- You must remain still and breathe normally to avoid distorted results.
After the Test:
- No recovery time needed; you can continue with your daily routine immediately.
- A cardiologist interprets and reports results to you.
How to read an ECG result?
Normal ECG Results:
- Heart rate: 60-100 BPM
- Normal rhythm (regular P-QRS-T waves)
- No ST-segment elevation/depression
Abnormal Findings on an ECG & Likely Causes:
- Bradycardia (<60 BPM): Due to either heart block or hypothyroidism.
- Tachycardia (>100 BPM): A symptom of stress, fever, or cardiial disease.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): Abnormal P waves, heightened stroke risk.
- ST-Segment Changes: Hints of heart attack or ischemia (inadequate blood flow).
- Prolonged QT Interval: Greater life-threatening arrhythmias risk.
What are the side effects of an ECG?
Electrocardiogram is extremely safe, with no radiation and no serious risks. But:
- A few patients may develop mild skin irritation from electrodes.
- A routine ECG does not rule out heart disease; further tests (e.g., an echocardiogram) may be needed.
Advanced ECG Technology: Dena Electrocardiograph Device
Dena electrocardiograph device is quite possibly the most comprehensive electrocardiogram test equipment on the market. The Dena model DG-7000 is completely PC-based for the utmost convenience of patients and healthcare professionals.
This device saves patient ECG test data and results, assisting doctors and medical professionals to conduct better and more accurate evaluations. In addition, it connects to computers via WiFi and USB and is capable of printing test results on regular printers.
Other Features:
Telecardiology: Remote diagnosis and monitoring.
Hospital View: Allows viewing the patient’s ECG from inside the hospital, useful when the patient is being transported in an ambulance and quick access is not possible.
Remote Results Transmission: Sends ECG results to doctors away from the hospital.
Mobile Access: Allows for the viewing of the ECG through a mobile phone.
Ambulance Usability: Can be used in ambulances for real-time monitoring.
For more information about the Dena electrocardiograph device, click here.