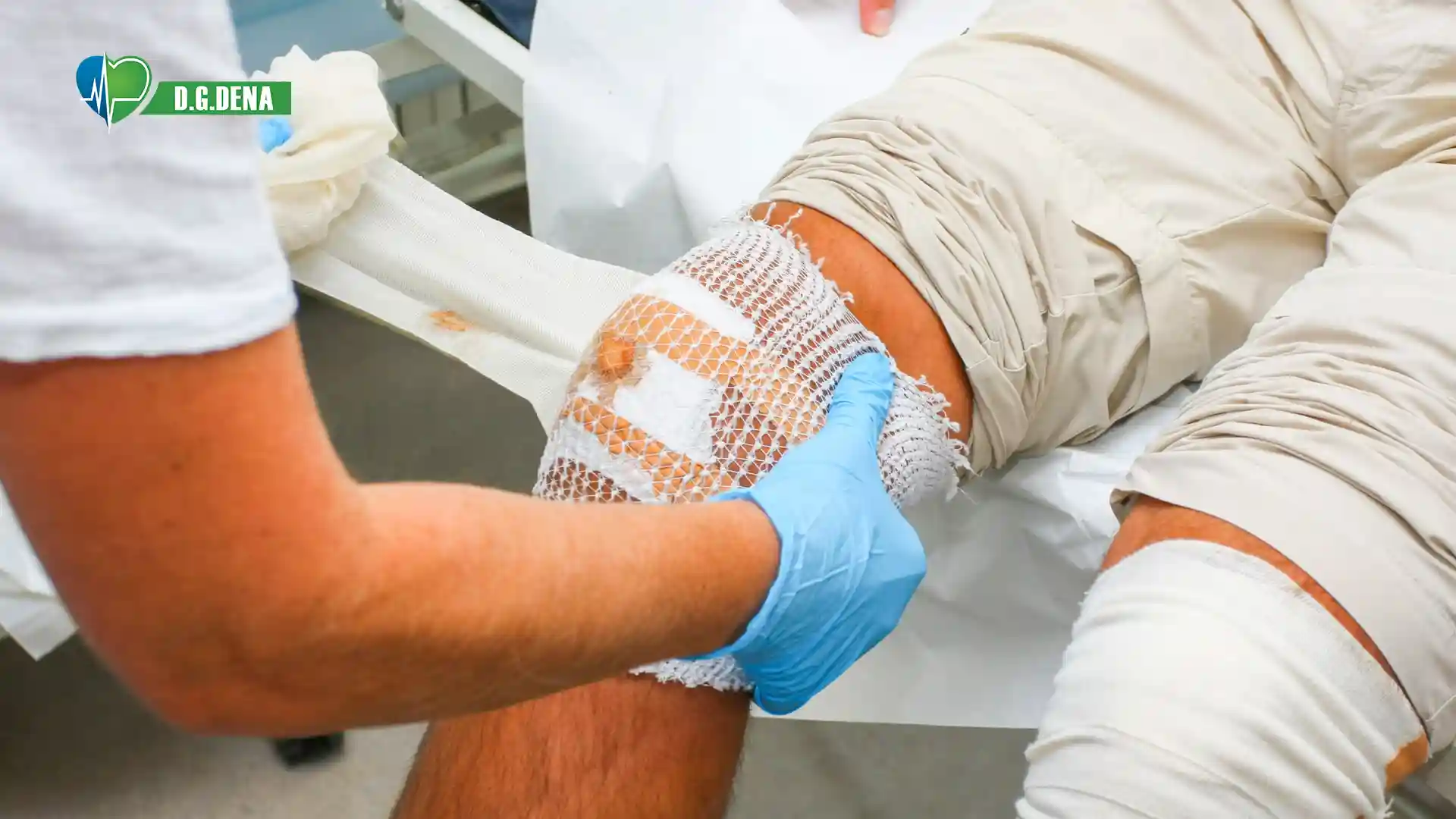
Wounds are inevitable in daily life, from minor kitchen cuts to more serious injuries. Proper wound disinfection prevents infection and speeds up wound healing. Even minor wounds can result in complications like delayed healing, scarring, or acute infection without proper wound disinfection or cleaning procedures.
Why Proper Wound Disinfecting Is Necessary?
Any break in the skin, whether a small cut, scrape, or surgical wound, requires proper care to prevent infection (wound disinfection) and promote healing. Otherwise, it can lead to:
- Local infections (redness, swelling, pus)
- Delayed wound healing
- Cellulitis (infectious skin pain)
- Sepsis (blood infection that can prove fatal)
Proper wound disinfection prevents:
- Destructive microbial growth
- Excessive inflammation
- Delay in tissue repair
- Scar formation
Wound Healing Phases
1. Hemostasis (blood clotting)
2. Inflammation (immune response)
3. Proliferation (tissue rebuilding)
4. Remodeling (scar maturation)
Proper wound care helps your body move smoothly through each healing stage for faster recovery.
Complete Guide to Cleaning a Wound
1- Preparation: Safety First
•Wash hands with soap and water thoroughly (or use hand sanitizer).
•Wear sterile gloves (if available) to prevent contamination.
2- Prepare Supplies
•Clean gauze or cloth
• Top wound disinfectant (e.g., saline solution, chlorhexidine)
• Antibiotic ointment (if needed)
• Sterile dressing or bandage
3- Stop the Bleeding (If Needed)
• Apply firm pressure with a clean cloth for 5–10 minutes.
• Consult a doctor if bleeding continues.
4- Clean the Wound
• Rinse with clean water or saline solution to remove dirt.
• Use a mild antiseptic (do not use hydrogen peroxide or rubbing alcohol).
• Wipe away dirt gently with sterile gauze (don’t scrub).
5- Apply an Antiseptic Solution
• Select mild disinfectants like povidone-iodine or polyhexanide (PHMB).
• Avoid harsh chemicals (e.g., alcohol preparations) that inhibit healing.
6- Dress the Wound
• Put a thin layer of antibiotic cream (for small cuts).
• Cover with sterile dressing or non-stick gauze.
7- Check for Infection
• Daily dressing change (or when wet/dirty).
• Watch for redness, swelling, or pus.
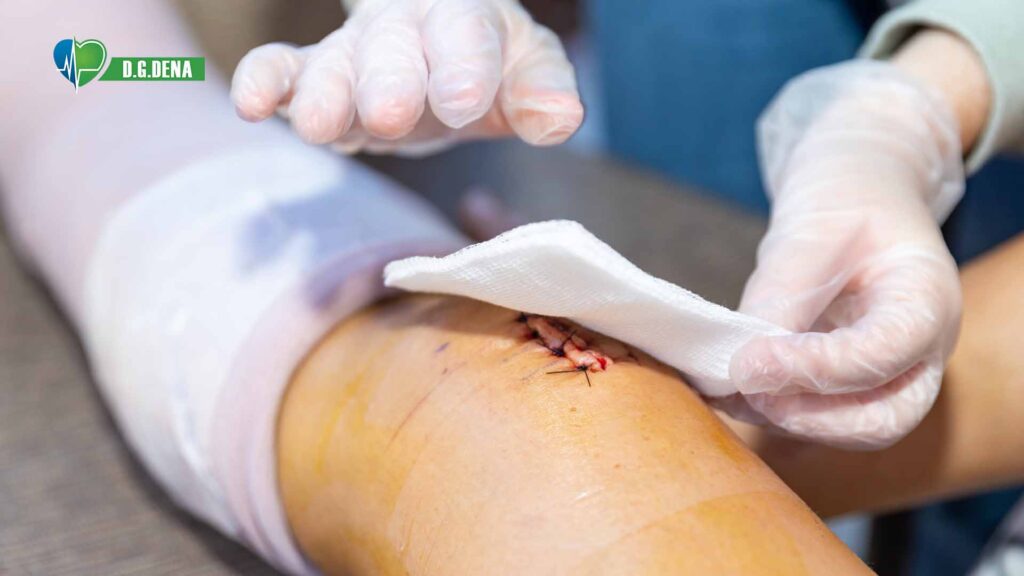
Dangerous Wound Disinfectants to Avoid
- Rubbing Alcohol: Destroys healthy tissue, extends healing.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Kills germs but harms new skin cells.
- Undiluted Essential Oils: Can lead to allergy or irritation.
Best Wound Disinfection Solutions Comparison
|
Solution |
Best For | Pros | Cons |
|
Saline Solution |
Gentle cleaning | Non-irritating, safe for all wounds |
No antimicrobial properties |
|
Povidone-Iodine (Betadine) |
Deep cuts, surgical wounds | Kills bacteria, viruses, and fungi |
Can stain skin, may irritate |
|
Chlorhexidine |
High-risk wounds | Long-lasting protection |
Can dry out skin |
|
Polyhexanide (PHMB) |
Chronic wounds, burns |
Promotes healing, gentle |
– |
| Antibiotic Ointments |
Minor cuts, scrapes |
Prevents bacterial growth |
Overuse can cause resistance |
When to Seek Medical Attention for Proper Wound Disinfection?
Visit a doctor if:
- Deep wounds will not close.
- Bleeding does not stop after 10 minutes.
- Infection signs appear (pus, fever, red streaks).
- Animal/human bites (high infection risk).
- Foreign objects (glass, metal) are lodged.
Tips for Faster Wound disinfection and cleansing
1- Keep the Wound Moist (Not Wet)
- Moist wounds heal faster than dry ones.
- Use hydrogel dressings for burns/deep wounds.
2- Eat a Healing-Friendly Diet
- Protein (tissue repair): Chicken, fish, beans.
- Vitamin C (collagen): Citrus, bell peppers.
- Zinc (immunity): Nuts, seeds, meat.
3- Avoid Smoking & Alcohol
- Both reduce blood flow, slowing healing.
4- Use Advanced Dressings (If Needed)
- Hydrocolloid dressings for oozing wounds.
- Silver dressings for infected wounds.
DG Derm Antimicrobial Wound Cleansing Solution, Advanced Wound Care
DG Derm Antimicrobial Wound Cleansing Solution is an extremely potent antimicrobial solution utilized for wound disinfection, irrigation, and moisturizing in acute and chronic wounds, such as burns. Its advanced composition is composed of polyhexanide (PHMB) and betaine, offering higher defense against infection and quicker healing.
Key Benefits & Mechanism of Action:
- Strong Antimicrobial Activity: Effectively kills a broad spectrum of bacteria (Gram-positive & Gram-negative), fungi, and resistant pathogens such as MRSA and VRE.
- Prevention & Disruption of Biofilms: Betaine reduces wound surface tension, deterring biofilm formation, a major cause of extended healing.
- Ideal Wound Moisturizing: Enables a moist wound-healing environment, which is critical for tissue regeneration.
Why Polyhexanide (PHMB) Stands Out in Wound Disinfection?
Current global studies position PHMB among the most effective antimicrobial agents in wound therapy because of its:
- Broad-spectrum efficacy against resistant microorganisms.
- Superior performance compared to traditional antiseptics.
- Global recognition as a first-line treatment for infection prevention and management.
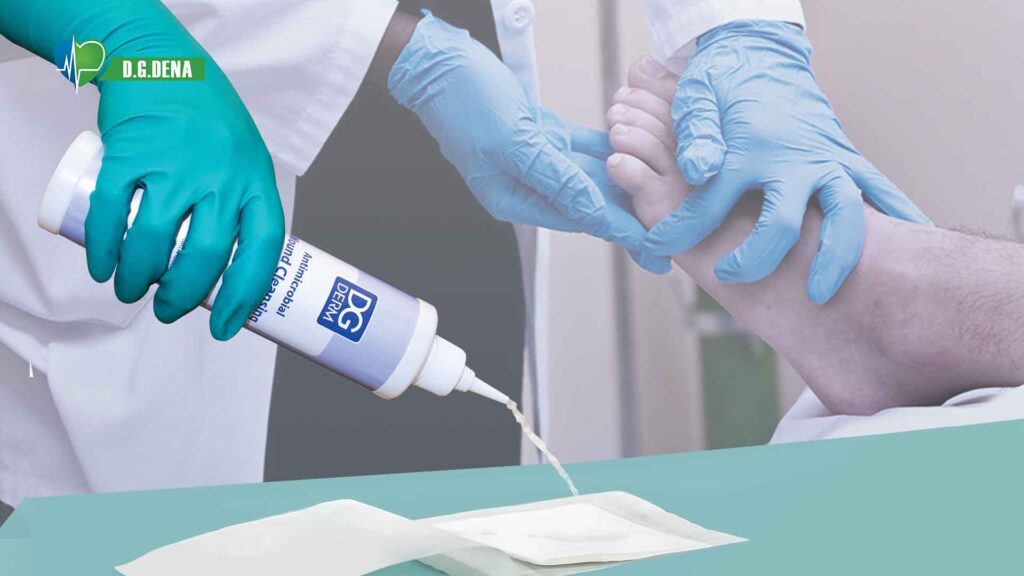
DG Derm’s PHMB solution is aligned with global wound care standards, offering clinically proven, safe, and effective wound management.
FAQs: Wound Disinfection
1- What’s the best disinfectant for open wounds?
PHMB-containing products (e.g., Prontosan) or povidone-iodine are safest.
2- Can I clean a wound with salt water?
Only sterile saline.
3- How do I know if a wound is infected?
Look for increased pain, redness, heat, pus, or fever.
4- Should wounds be allowed to breathe during healing?
Yes, but only after initial healing (keep covered for 2–3 days).
5- What’s the safest way to disinfect a wound at home?
For proper wound disinfection, follow these steps:
- Clean gently with sterile saline or mild antiseptics like povidone-iodine or polyhexanide (PHMB).
- Avoid harsh agents like hydrogen peroxide or rubbing alcohol—they damage healing tissue.
- Cover with a sterile dressing to protect against bacteria while keeping the wound moist.
Conclusion
Choosing the best wound disinfectant and taking good wound care ensures rapid healing and prevents infection. Remember:
- Clean carefully (not with alcohol/peroxide).
- Keep it wet (use proper dressings).
- Monitor for infection.
- See a doctor if needed.